Anúncios
Lab-grown meat, or cultured meat, is an innovation that promises to transform the food industry. Using a cellular agriculture process, it offers a more ethical and environmentally responsible alternative to conventional meat. This technology is increasingly being considered a sustainable solution to the growing demand for food worldwide.
Produced without the need to raise and slaughter animals, lab-grown meat emerges as a response to the negative impacts of livestock farming. With benefits for both health and the environment, it has the potential to change the way we consume protein. Understanding how this technology works is essential to exploring its many advantages.
Anúncios

The Process of Producing Lab-Grown Meat
Lab-grown meat is produced through cellular agriculture, a highly technical process. Initially, animal stem cells are collected from a living animal without causing harm. These cells are then cultivated in a controlled environment where they multiply and form muscle tissue, mimicking the natural process of meat growth.
The cultivation environment consists of essential nutrients that the cells need to grow. Through bioreactors, these cells develop, giving rise to muscle fibers that can be transformed into food products. This entire process is closely monitored to ensure that the final meat is safe and has the texture and taste of traditional meat.
Tissue engineering is fundamental to the success of lab-grown meat. Scientists work to replicate the natural structure of meat by adjusting variables such as the cultivation environment and nutrients. This ongoing refinement aims to improve the sensory experience of the consumer and make lab-grown meat a viable option for the market.
Unlike conventional meat, lab-grown meat production does not require the raising of entire animals. This results in a significantly lower environmental impact, reducing the need for large areas of land and intensive use of natural resources such as water and feed.
How Lab-Grown Meat Works: Understanding the Science Behind Cellular Agriculture
Lab-grown meat, also known as cultured meat or cell-based meat, is produced through a process called cellular agriculture. This innovative method involves collecting a small sample of animal cells, typically muscle cells, and cultivating them in a controlled environment. The cells are provided with the necessary nutrients to grow and multiply, forming muscle tissue that resembles conventional meat. This process eliminates the need to raise and slaughter animals, while addressing various ethical and environmental concerns associated with traditional meat production.
The science behind lab-grown meat is based on tissue engineering and bioprocessing techniques. Initially, scientists isolate stem cells from a living animal, often through a painless biopsy. These cells are placed in a nutrient-rich culture medium containing amino acids, vitamins, and minerals. The cells proliferate and differentiate into muscle fibers, which can be harvested and processed into various meat products. The entire process is designed to mimic the natural growth of muscle tissue, ensuring that the final product is safe for human consumption and resembles the taste and texture of conventional meat.
As the technology advances, researchers are exploring different methods to enhance the flavor, texture, and nutritional profile of lab-grown meat. This includes the incorporation of fats and connective tissues, which play a crucial role in the sensory experience of consuming meat. By adjusting these elements, lab-grown meat can attract a wider audience, including those who are currently skeptical about its viability as a substitute for traditional meat.
Additionally, lab-grown meat has the potential to revolutionize the food industry by offering a more sustainable and ethical alternative to conventional meat production. With the global population projected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050, the demand for protein sources will only increase. Lab-grown meat provides a solution that could help meet this demand while significantly reducing the environmental impact associated with livestock farming, such as greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption.
Advantages of Lab-Grown Meat as a Sustainable Food Option
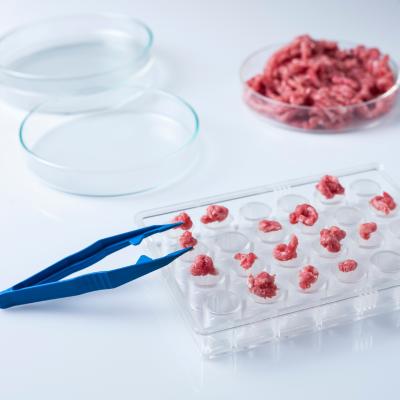
The advantages of lab-grown meat go beyond ethical considerations; they encompass a wide range of benefits that contribute to a more sustainable food system. One of the most significant advantages is the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Traditional livestock farming is a major contributor to climate change, with methane emissions from ruminant animals being particularly problematic. In contrast, the production of lab-grown meat generates significantly lower emissions, making it a more climate-friendly option.
Another key advantage is the efficient use of resources. Conventional meat production requires vast amounts of land, water, and feed to raise animals. In contrast, lab-grown meat requires fewer resources since it eliminates the need to raise and feed livestock. This efficiency not only helps conserve natural resources but also reduces pressure on ecosystems that are often affected by livestock farming.
Lab-grown meat can also improve food security. With the growing global population and increasing demand for protein, lab-grown meat could provide a reliable and consistent source of high-quality protein. It can be produced in urban areas, reducing the need for transportation and ensuring that fresh meat is available to consumers more affordably. This localized production can help address food deserts and improve access to nutritious food in underserved communities.
Furthermore, lab-grown meat can be tailored to meet specific dietary needs and preferences. For example, it could be designed to contain higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids or lower levels of saturated fat, appealing to health-conscious consumers. This customization could lead to healthier eating habits and contribute to overall public health.
Finally, lab-grown meat aligns with the growing consumer demand for transparency and sustainability in food production. As more people become aware of the environmental and ethical implications of their food choices, lab-grown meat offers a solution that addresses these concerns. By choosing lab-grown meat, consumers can enjoy the taste and texture of traditional meat while supporting a more sustainable and humane food system.
How to Incorporate Lab-Grown Meat Into Your Diet
Lab-grown meat offers a unique opportunity for consumers to diversify their diets while making more sustainable food choices. Here are some ways to incorporate lab-grown meat into your meals:
- Explore different lab-grown meat products available on the market. As the technology advances, various companies are developing lab-grown meat products, including burgers, sausages, and chicken nuggets. Familiarizing yourself with these options can help you find your favorites and make informed choices when shopping.
- Consider recipes that include lab-grown meat for everyday meals. Just like traditional meat, lab-grown meat can be used in a wide variety of recipes, from stir-fries to pasta dishes. Experimenting with different cooking methods and flavor profiles can help you discover new ways to enjoy lab-grown meat in your meals.
- Learn about the nutritional benefits of lab-grown meat. Many lab-grown meat products are designed to be nutritionally comparable to their conventional counterparts, providing essential nutrients such as protein, iron, and B vitamins. Understanding these benefits can help you make healthier choices when planning your meals.
- Understand the environmental benefits of choosing lab-grown meat. By opting for lab-grown meat, you are actively supporting a more sustainable food system that reduces greenhouse gas emissions and conserves natural resources. This knowledge can enhance your appreciation for the food you consume and motivate you to make more environmentally conscious choices.
- Discover how lab-grown meat can contribute to food security. As lab-grown meat becomes more widely available, it has the potential to improve access to nutritious food, particularly in urban areas where fresh meat may be scarce. Supporting this industry can help create a more resilient food system that meets the needs of a growing population.
- Stay informed about the latest advancements in clean meat technology. The field of cellular agriculture is rapidly evolving, with new developments and innovations emerging regularly. Keeping up with these advancements can help you stay informed about the benefits and potential of lab-grown meat as a sustainable food option.
Lab-grown meat offers a promising solution to many of the challenges associated with traditional meat production. By embracing this innovative food option, consumers can enjoy delicious meals while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Did You Enjoy Learning About Lab-Grown Meat as a Sustainable Food Option?
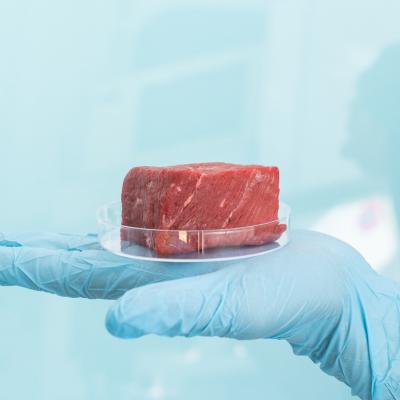
Lab-grown meat represents a significant step toward a more sustainable food system. As we continue to explore and understand its benefits, we can make informed choices that positively impact our planet and our health.
The future of food is evolving, and lab-grown meat is at the forefront of this transformation. Stay curious and keep learning about this exciting development in sustainable agriculture!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is lab-grown meat?
Lab-grown meat is made from animal cells. These cells grow in a controlled environment.
Is lab-grown meat healthy?
Yes! It can be healthier than traditional meat. It contains less fat and may have more nutrients.
Is lab-grown meat a sustainable option?
Yes, lab-grown meat as a sustainable option reduces the use of natural resources and emits fewer gases.
How is lab-grown meat made?
Animal cells are collected and fed in a bioreactor. This helps them grow and transform into meat.
Will lab-grown meat replace conventional meat?
Perhaps! It could be a viable alternative in the future. This depends on pricing and consumer acceptance.
